Last Update 5 hours ago Total Questions : 90
The API 580 - Risk Based Inspection content is now fully updated, with all current exam questions added 5 hours ago. Deciding to include API-580 practice exam questions in your study plan goes far beyond basic test preparation.
You'll find that our API-580 exam questions frequently feature detailed scenarios and practical problem-solving exercises that directly mirror industry challenges. Engaging with these API-580 sample sets allows you to effectively manage your time and pace yourself, giving you the ability to finish any API 580 - Risk Based Inspection practice test comfortably within the allotted time.
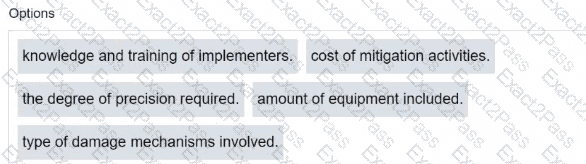
The resources and time required to implement an RBI assessment will vary widely between organizations depending on a number of factors including:
Which of the following is the act of mitigating a particular risk?
Which of the following statements is accurate regarding data quality relative to the type of RBI assessment selected?
Which of the following may make it impractical to reduce some risks to an acceptable level?
Which of the following is a step in estimating the consequences of releasing a hazardous material into the surrounding environment?
Conducting more internal inspection than is called for by RBI:
The fact that some jurisdictions may have some prescriptive time-based rules on inspection intervals does not preclude the user from gaining significant benefits from the application of RBI, as long as:

