Last Update 20 hours ago Total Questions : 269
The Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions content is now fully updated, with all current exam questions added 20 hours ago. Deciding to include 300-510 practice exam questions in your study plan goes far beyond basic test preparation.
You'll find that our 300-510 exam questions frequently feature detailed scenarios and practical problem-solving exercises that directly mirror industry challenges. Engaging with these 300-510 sample sets allows you to effectively manage your time and pace yourself, giving you the ability to finish any Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions practice test comfortably within the allotted time.
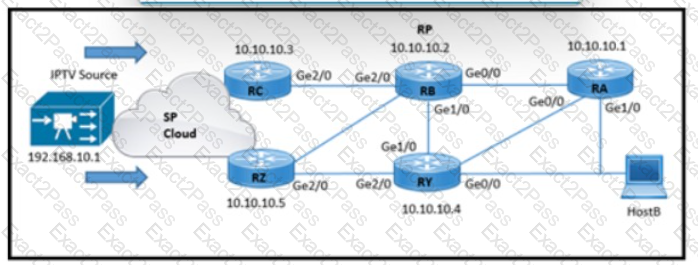
Refer to the exhibit. HostB receives an IPTV traffic stream from the multicast source at 192.168 10.1. When router RB is powered down, it impacts multicast traffic forwarding to downstream peers. The RA and RB routers reside in the same physical location. Which two configurations must be implemented so that HostB receives the multicast stream even when RB is powered down? (Choose two )
Refer to the exhibits.
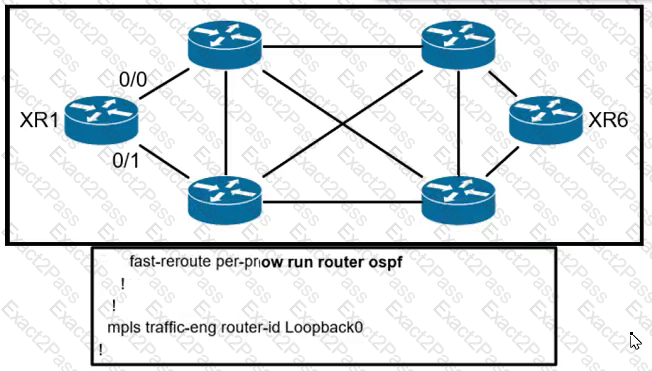
All links inside the network are configured at a default cost of one inside the fully converged OSPF domain. Given the configuration from XR1, which interface does traffic from XR1 that is destined to the loopback interface of XR6 select for the exiting interface?
Which two differences should be considered when deciding whether to implement to implement routing policies or route maps? (Choose two.)
Guidelines
This is a lab item in which tasks will be performed on virtual devices.
Refer to the Tasks tab to view the tasks for this lab item.
Refer to the Topology tab to access the device console(s) and perform the tasks.
Console access is available for all required devices by clicking the device icon or using the tab(s) above the console window.
All necessary preconfigurations have been applied.
Do not change the enable password or hostname for any device.
Save your configurations to NVRAM before moving to the next item.
Click Next at the bottom of the screen to submit this lab and move to the next question.
When Next is clicked, the lab doses and cannot be reopened.
Topology
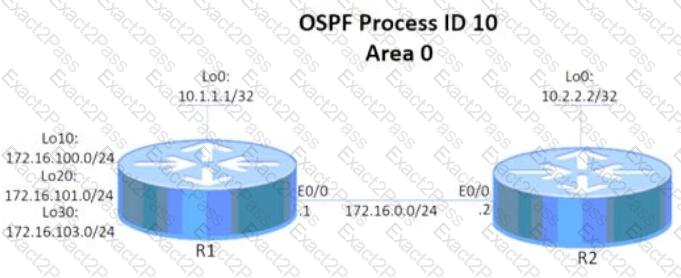
Tasks
Configure and verify an OSPF neighbor adjacency between R1 and R2 in OSPF area 0 according to the topology to achieve these goals:
1. R1 pings the Loopback0 interface of R2. Use interface-level configuration to complete this task.
2. R2 pings the Loopback0 interface of R1. Use interface-level configuration to complete this task.
3. R2 receives a single summary route 172.16.100.0/22 for networks 172.16.100.0/24, 172.16.101.0/24, and 172.16.103.0/24.
For which reason can two devices fail to establish an OSPF neighbor relationship?
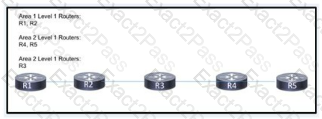
Refer to the exhibit. This network is deployed with all connected links configured to run IS-IS. The routing protocol is enacted globally on each router, and the network engineer expects full routing Information to be shared among all routers. R5 is receiving routes from R4 but is missing routes from R1. Which action corrects the issue so that all routes are shared among the routers?
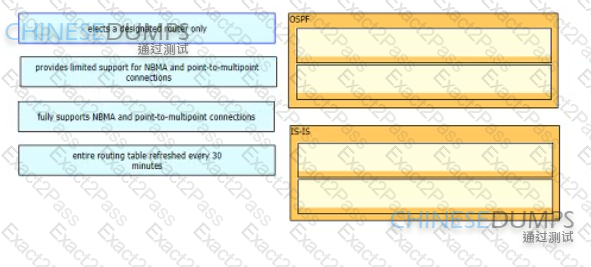
Drag and drop the features from the left onto the corresponding routing protocols on the right