Last Update 8 hours ago Total Questions : 165
The Abdomen Sonography Examination content is now fully updated, with all current exam questions added 8 hours ago. Deciding to include AB-Abdomen practice exam questions in your study plan goes far beyond basic test preparation.
You'll find that our AB-Abdomen exam questions frequently feature detailed scenarios and practical problem-solving exercises that directly mirror industry challenges. Engaging with these AB-Abdomen sample sets allows you to effectively manage your time and pace yourself, giving you the ability to finish any Abdomen Sonography Examination practice test comfortably within the allotted time.
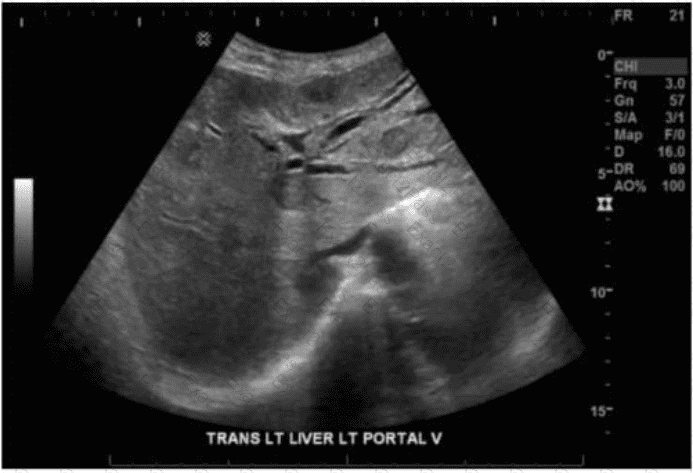
Which sonographic appearance of the bile ducts is demonstrated in this image?
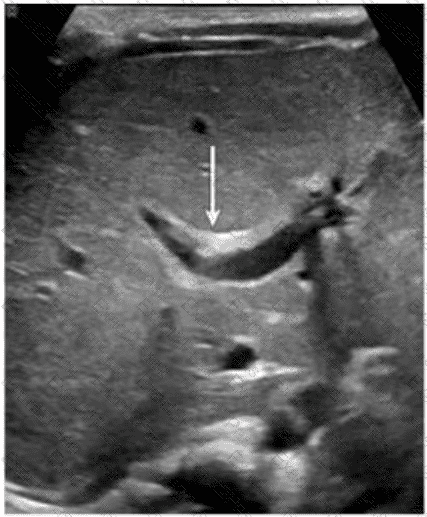
Which congenital disorder is most consistent with the finding identified by the arrow on this image?
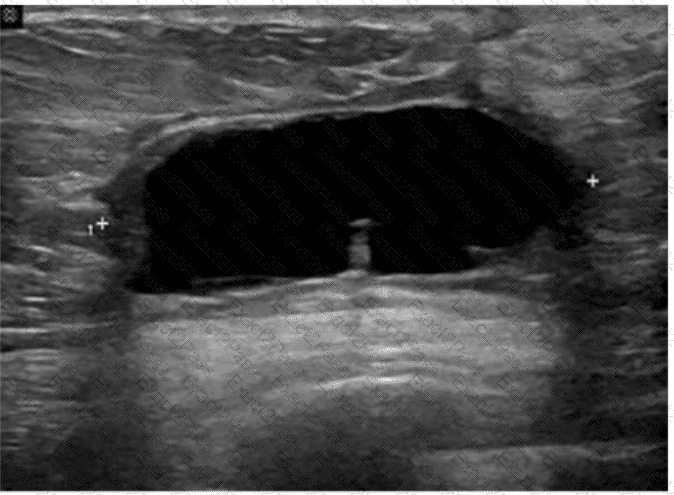
Which condition is most consistent with this image of a postsurgical breast?
Which of the following must be sterile for a percutaneous procedure?
Which retroperitoneal finding is most likely associated with trauma?
Which arteries are the immediate branches of the celiac trunk?
Which vessel is located directly proximal to the origination of the renal arteries?

