Last Update 19 hours ago Total Questions : 38
The FCSS - Public Cloud Security 7.6 Architect content is now fully updated, with all current exam questions added 19 hours ago. Deciding to include FCSS_CDS_AR-7.6 practice exam questions in your study plan goes far beyond basic test preparation.
You'll find that our FCSS_CDS_AR-7.6 exam questions frequently feature detailed scenarios and practical problem-solving exercises that directly mirror industry challenges. Engaging with these FCSS_CDS_AR-7.6 sample sets allows you to effectively manage your time and pace yourself, giving you the ability to finish any FCSS - Public Cloud Security 7.6 Architect practice test comfortably within the allotted time.
Refer to the exhibit.
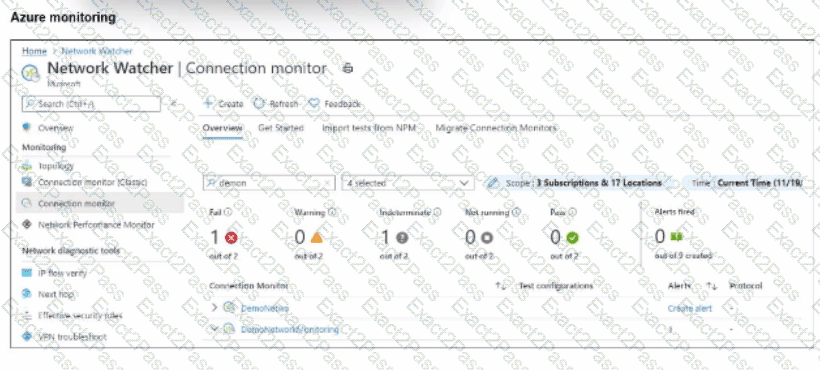
After analyzing the native monitoring tools available in Azure, an administrator decides to use the tool displayed in the exhibit.
Why would an administrator choose this tool?
Refer to the exhibit.

You deployed a FortiGate HA active-passive cluster in Microsoft Azure.
Which two statements regarding this particular deployment are true? (Choose two.)
An administrator would like to use FortiCNP to keep track ofsensitive data files located in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3bucket and protect it from malware. Which FortiCNP feature should the administrator use?
Refer to the exhibit.

You are managing an active-passive FortiGate HA cluster in AWS that was deployed using CloudFormation. You have created a change set to examine the effects of some proposed changes to the current infrastructure. The exhibit shows some sections of the change set.
What will happen if you apply these changes?
An administrator is relying on an Azure Bicep linter to find possible issues in Bicep files.
Which problem can the administrator expect to find?
An AWS administrator must ensure that each member of the cloud deployment team has the correct permissions to deploy and manage resources using CloudFormation. The administrator is researching which tasks must be executed with CloudFormation and therefore require CloudFormation permissions.
Which task is run using CloudFormation?
What would be the impact of confirming to delete all the resources in Terraform?


